CAN Usage
1. CAN Introduction
CAN (Controller Area Network): A serial communication network that effectively supports distributed control or real-time control.
Currently, most automobile manufacturers in the world adopt the CAN bus to achieve data communication between internal control systems of automobiles.
RK3568/RK3588 CAN driver file: drivers/net/can/rockchip/rockchip_canfd.c
In the ArmSoM-Sige7, CAN is integrated into the 40PIN, which can be reused by users as CAN-related pins.
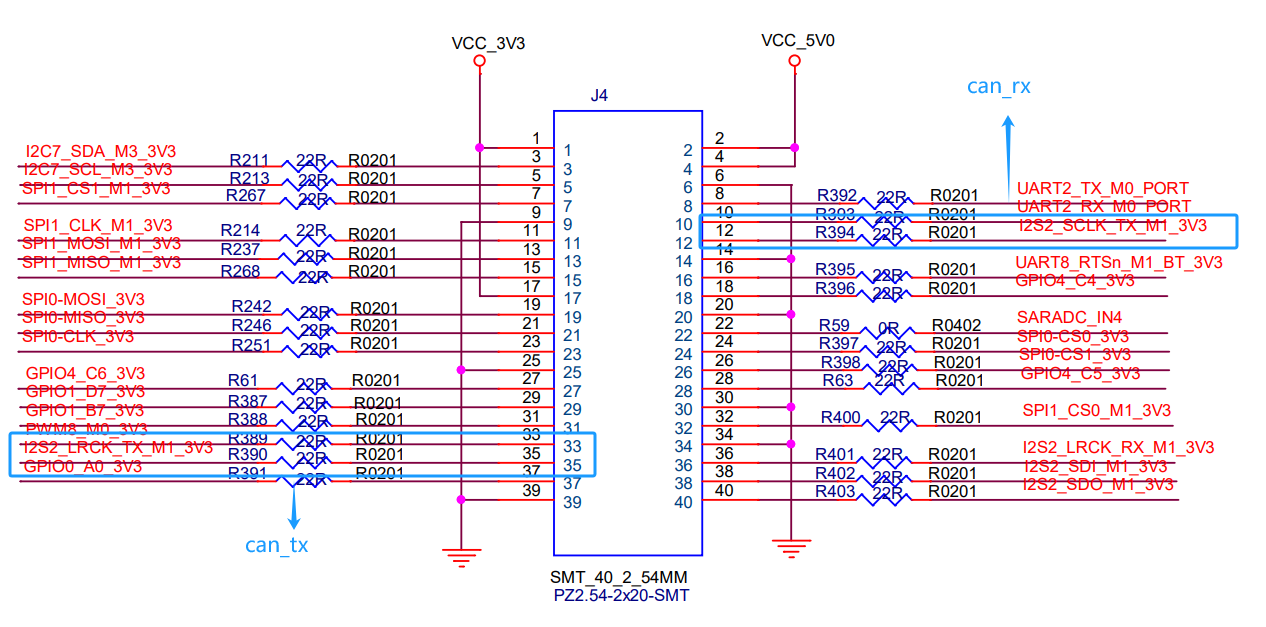
2. Schematic Diagram
Location of CAN in 40PIN: CAN_TX corresponds to pin 35 in 40PIN, and CAN_RX corresponds to pin 12 in 40PIN.
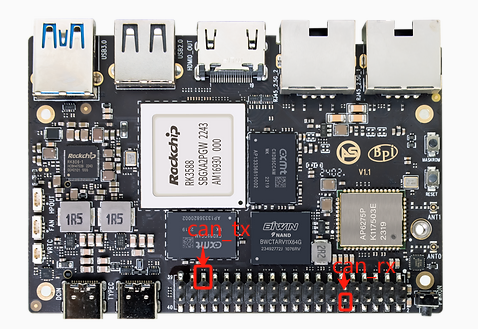
3. Hardware Connection
CAN module wiring: CAN_TX connects to CAN_TX, CAN_RX connects to CAN_RX.
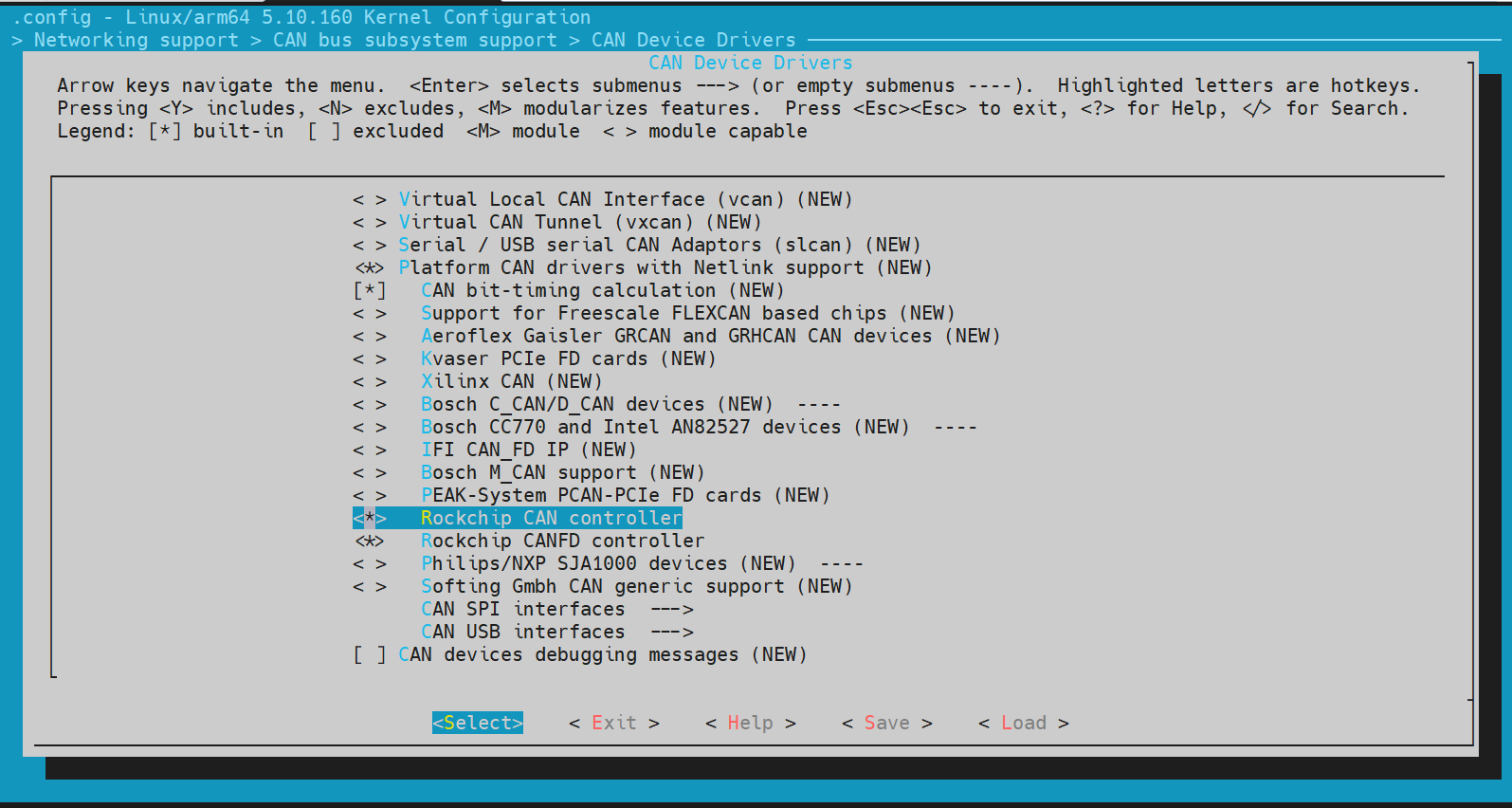
4. Kernel Configuration
- rockchip_linux_defconfig configuration:
CONFIG_CAN=y
CONFIG_CAN_DEV=y
CONFIG_CAN_ROCKCHIP=y
CONFIG_CANFD_ROCKCHIP=y
- Kernel configuration:
cd kernel
make ARCH=arm64 menuconfig
make savedefconfig
- Select: Networking support ---> CAN bus subsystem support ()--->CAN Device Drivers() ---> Platform CAN drivers with Netlink support(*)
5. DTS Node Configuration
5.1 Main Parameters:
interrupts Generates an interrupt signal upon completion of transfer.
clock Clock attribute, used to turn on/off clk; reset attribute, used to reset the bus each time.
pinctrl Configures CAN-related pin information and function multiplexing.
5.2 Chip-level Common Configuration
kernel-5.10/arch/arm64/boot/dts/rockchip/rk3588s.dtsi
can0: can@fea50000 {
compatible = "rockchip,can-2.0";
reg = <0x0 0xfea50000 0x0 0x1000>;
interrupts = <GIC_SPI 341 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH>;
clocks = <&cru CLK_CAN0>, <&cru PCLK_CAN0>;
clock-names = "baudclk", "apb_pclk";
resets = <&cru SRST_CAN0>, <&cru SRST_P_CAN0>;
reset-names = "can", "can-apb";
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&can0m0_pins>;
tx-fifo-depth = <1>;
rx-fifo-depth = <6>;
status = "disabled";
};
can1: can@fea60000 {
compatible = "rockchip,can-2.0";
reg = <0x0 0xfea60000 0x0 0x1000>;
interrupts = <GIC_SPI 342 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH>;
clocks = <&cru CLK_CAN1>, <&cru PCLK_CAN1>;
clock-names = "baudclk", "apb_pclk";
resets = <&cru SRST_CAN1>, <&cru SRST_P_CAN1>;
reset-names = "can", "can-apb";
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&can1m0_pins>;
tx-fifo-depth = <1>;
rx-fifo-depth = <6>;
status = "disabled";
};
can2: can@fea70000 {
compatible = "rockchip,can-2.0";
reg = <0x0 0xfea70000 0x0 0x1000>;
interrupts = <GIC_SPI 343 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH>;
clocks = <&cru CLK_CAN2>, <&cru PCLK_CAN2>;
clock-names = "baudclk", "apb_pclk";
resets = <&cru SRST_CAN2>, <&cru SRST_P_CAN2>;
reset-names = "can", "can-apb";
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&can2m0_pins>;
tx-fifo-depth = <1>;
rx-fifo-depth = <6>;
status = "disabled";
};
compatible = "rockchip,can-1.0" is used to match the can controller driver.
compatible = "rockchip,can-2.0" is used to match the canfd controller driver.
assigned-clock-rates is used to configure the constant frequency of the can. If the CAN bit rate is less than or equal to 3M, it is recommended to modify the CAN clock to 100M for more stable signals. For bit rates higher than 3M, a clock setting of 200M is sufficient.
pinctrl configuration: Based on the actual board connection, configure the iomux of can_h and can_l for the can function.
5.3 Board-level Configuration
kernel-5.10/arch/arm64/boot/dts/rockchip/rk3588-armsom-w3.dts
/* can1 */
&can1 {
status = "okay";
assigned-clocks = <&cru CLK_CAN1>;
assigned-clock-rates = <200000000>;
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&can1m1_pins>; #Configure based on the schematic diagram
};
- Since the CAN device created by the system according to the above dts node is only one, and the first created device is CAN0.
6. CAN Communication Test
- Query current network devices:
ifconfig -a
- CAN startup
ip link set can0 down //Close CAN
ip link set can0 type can bitrate 500000 #Set bit rate to 500KHz
ip -details -statistics link show can0 #Print can0 information
ip link set can0 up //Start CAN
- CAN send
cansend can0 123#DEADBEEF #Send (standard frame, data frame, ID:123, data:DEADBEEF)
cansend can0 123#R #Send (standard frame, remote frame, ID:123)
cansend can0 00000123#12345678 #Send (extended frame, data frame, ID:00000123, data:DEADBEEF)
cansend can0 00000123#R #Send (extended frame, remote frame, ID:00000123)
- CAN receive
candump can0 //candump can0